基于单碱基替换的iSTOP基因敲除技术
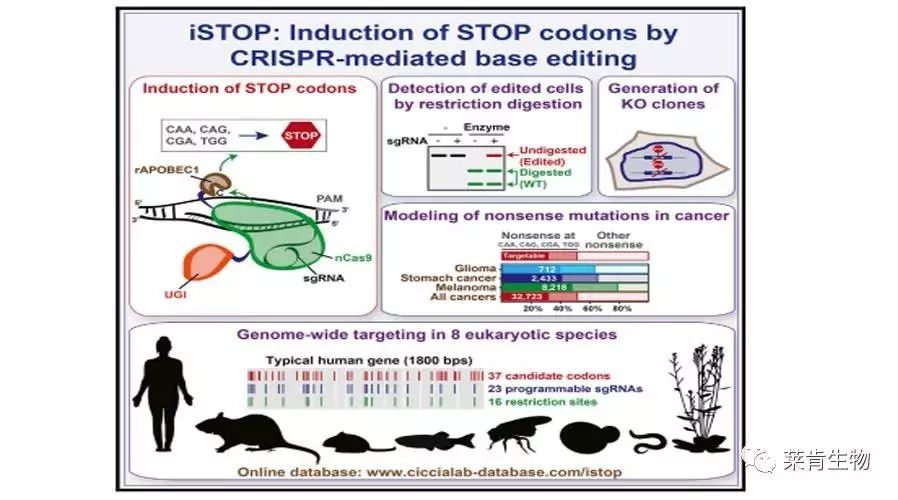
基因编辑技术可以通过单碱基替换创造终止密码子的形式实现基因敲除。最近,美国哥伦比亚大学的科学家创立了一个名为iSTOP的基因编辑技术和数据库,可以实现8种模式生物的基因突变。
iSTOP是利用基于胞苷脱氨酶(cytidine deaminase)的CRISPR编辑体系,造成C > T的碱基替换,从而实现四种密码子CAA、CAG、CGA和TGG转变为终止密码子TAA、TAG和TGA。为了增加iSTOP技术的使用便利性并扩大应用领域,研究人员创办了一个在线数据库(http://www.ciccialab-database.com/istop),使得iSTOP技术能够应用到8种真核生物中,包括人、小鼠、大鼠、斑马鱼、线虫、果蝇、拟南芥、酵母。该数据库包含340万个sgRNA,涵盖了这些物种97-99%的基因,由此可见iSTOP技术的应用广度。此外,研究人员还开发了针对性的RFLP编辑位点检测技术,以方便快速鉴定突变位点。而脱靶概率预测、靶标异构体分析、无义突变衰减预测等功能可以优化sgRNA的设计。
除了方便基因功能研究,该数据库提供的3.2万个癌症相关位点编辑模型,将给精准医疗领域带来巨大的价值。
Molecular Cell, 7 September 2017
CRISPR-Mediated Base Editing Enables Efficient Disruption of Eukaryotic Genes through Induction of STOP Codons
Author
Pierre Billon, Eric E. Bryant, Sarah A. Joseph, Tarun S. Nambiar, Samuel B. Hayward, Rodney Rothstein, Alberto Ciccia*
*: Department of Genetics and Development, Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center, Columbia University Medical Center, USA
Summary
Standard CRISPR-mediated gene disruption strategies rely on Cas9-induced DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Here, we show that CRISPR-dependent base editing efficiently inactivates genes by precisely converting four codons (CAA, CAG, CGA, and TGG) into STOP codons without DSB formation. To facilitate gene inactivation by induction of STOP codons (iSTOP), we provide access to a database of over 3.4 million single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) for iSTOP (sgSTOPs) targeting 97%–99% of genes in eight eukaryotic species, and we describe a restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) assay that allows the rapid detection of iSTOP-mediated editing in cell populations and clones. To simplify the selection of sgSTOPs, our resource includes annotations for off-target propensity, percentage of isoforms targeted, prediction of nonsense-mediated decay, and restriction enzymes for RFLP analysis. Additionally, our database includes sgSTOPs that could be employed to precisely model over 32,000 cancer-associated nonsense mutations. Altogether, this work provides a comprehensive resource for DSB-free gene disruption by iSTOP.