基因表达调控在控制植物表型和适应性方面发挥重要作用
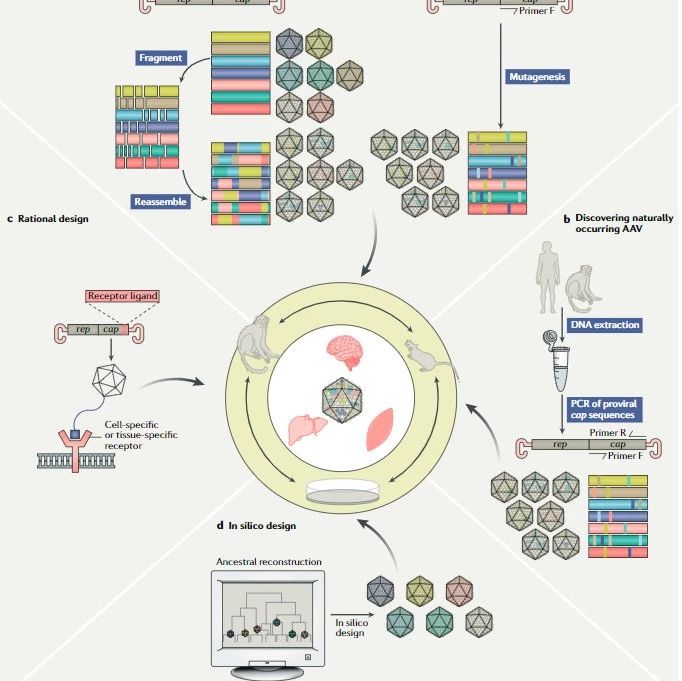
基因表达调控在控制植物表型和适应性方面发挥重要作用。近日,中国农业大学田丰和美国威斯康辛大学的研究团队通过综合分析玉米与其祖先种大刍草杂交衍生得到的回交重组自交系群体的基因表达变异特征,揭示了玉米驯化过程对基因表达的影响及其调控的分子遗传基础。研究运用全基因组图谱技术鉴定得到17311个基因的25600个eQTL(表达数量性状基因座),并发现了较大程度的表达差异。相邻基因之间更容易发生近端eQTL(local-eQTL),这些基因具有相同的表达方式,从而形成共同调控的同类基因族。该类基因大都功能相关且共享染色质修饰。远端-eQTL(disant-eQTL)在特定功能域内发现了调节7156个目标基因的125个重要位点。通过信息分析推断得到一系列代谢路径的反式调节器。其中bHLH和己糖激酶的转录因子R1和hex9可能分别在黄酮类物质的合成和糖降解过程中发挥了关键作用。
本文揭示了驯化或进化进程中对对目标基因的选择作用和对基因表达的重要影响。对玉米育种具有重要的启发和指导意义。
MOLECULAR PLANT , 22 December 2017
Genome-wide analysis of transcriptional variability in a large maize-teosinte Population
Authors
Xufeng Wang, Qiuyue Chen, Yaoyao Wu, ……Dan Li, John F. Doebley, Feng Tian
National Maize Improvement Center Of China, Beijing Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Laboratory of Crop Heterosis and Utilization, Joint International Research Laboratory of Crop Molecular Breeding, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193,China
Abstract
The regulation of gene expression plays an important role in controlling plant phenotypes and adaptation. Here, we report a comprehensive assessment of gene expression variation by sequencing the transcriptome of a large maize-teosinte experimental population. Genome-wide mapping identified 25,660 expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) for 17,311 genes, capturing an unprecedented range of expression variation. We found that local-eQTL more frequently mapped to adjacent genes, displaying a mode of expression piggybacking, which consequently created co-regulated gene clusters. Genes within the co-regulated gene clusters tend to have related function and shared chromatin modification. Distant-eQTL formed 125 significant distant-eQTL hotspots with their targets significantly enriched in specific functional categories. By integrating different sources of information,we identified putative trans-regulators for a variety of metabolic pathways. We demonstrated that the bHLH transcription factor R1 and hexokinase hex9 might act as crucial regulators for flavonoid biosynthesis and glycolysis, respectively. Finally, we showed that domestication or improvement has significantly impacted global gene expression, with many genes targeted by selection. Of particular interest, the Bx genes for benzoxazinoid biosynthesis may have undergone coordinated cis-regulatory divergence between maize and teosinte. We further demonstrated that a transposon insertion that inactivates Bx12 was under strong selection as maize spread into temperate environments with a distinct herbivore community.
来源:网络
声明:本公号所载内容来源于互联网、微信公众号等公开渠道,不代表本公号观点,仅为交流学习所用。本文来源若标注错误或侵犯到您的权利,烦请告知,我们将立即删除,并在下一日发布更正或致歉公