基因突变携带者能否进行保乳手术
众所周知,生殖细胞乳腺癌易感基因(BRCA)突变与乳腺癌发生风险密切相关。不过,目前尚不明确BRCA突变携带者是否属于保乳手术禁忌证。
2019年3月20日,施普林格·自然旗下《乳腺癌研究与治疗》在线发表北京大学肿瘤医院曹威、解云涛、何英剑、李金锋、王天峰、范照青、范铁、欧阳涛等学者的研究报告,回顾分析了BRCA突变状态是否影响中国女性原发浸润乳腺癌保乳手术后同侧乳腺肿瘤复发率。
该单中心回顾研究将2001年11月~2017年4月北京大学肿瘤医院1947例中国女性原发浸润乳腺癌保乳手术患者按BRCA突变状态分为携带者组103例和非携带者组1844例,分析同侧乳腺肿瘤复发率与BRCA突变的相关性。同侧乳腺肿瘤复发病例进一步分为新原发肿瘤和真局部复发。通过多因素比例风险回归模型,分析新原发肿瘤风险因素。
结果,BRCA突变携带者与非携带者相比:
-
年龄较小(P<0.001)
-
HER2阴性比例较高(P=0.01)
-
肿瘤>2cm比例较高(P=0.04)
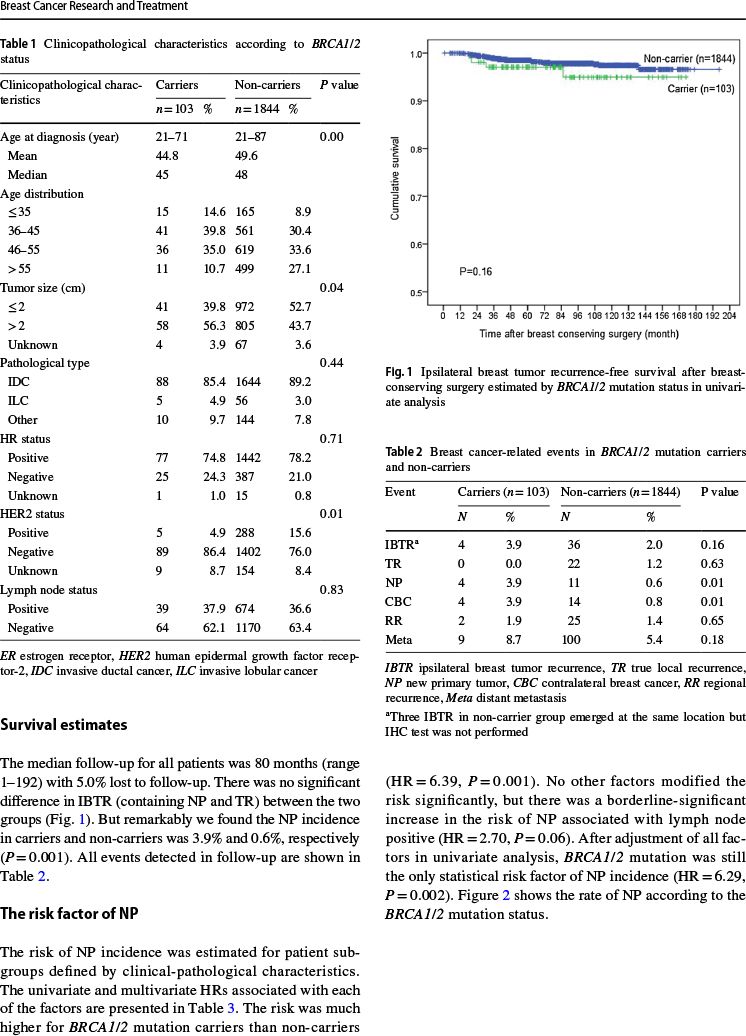
所有患者中位随访80个月期间,BRCA突变携带者与非携带者相比:
-
同侧乳腺肿瘤复发率相似:3.9%比2.0%(P=0.16)
-
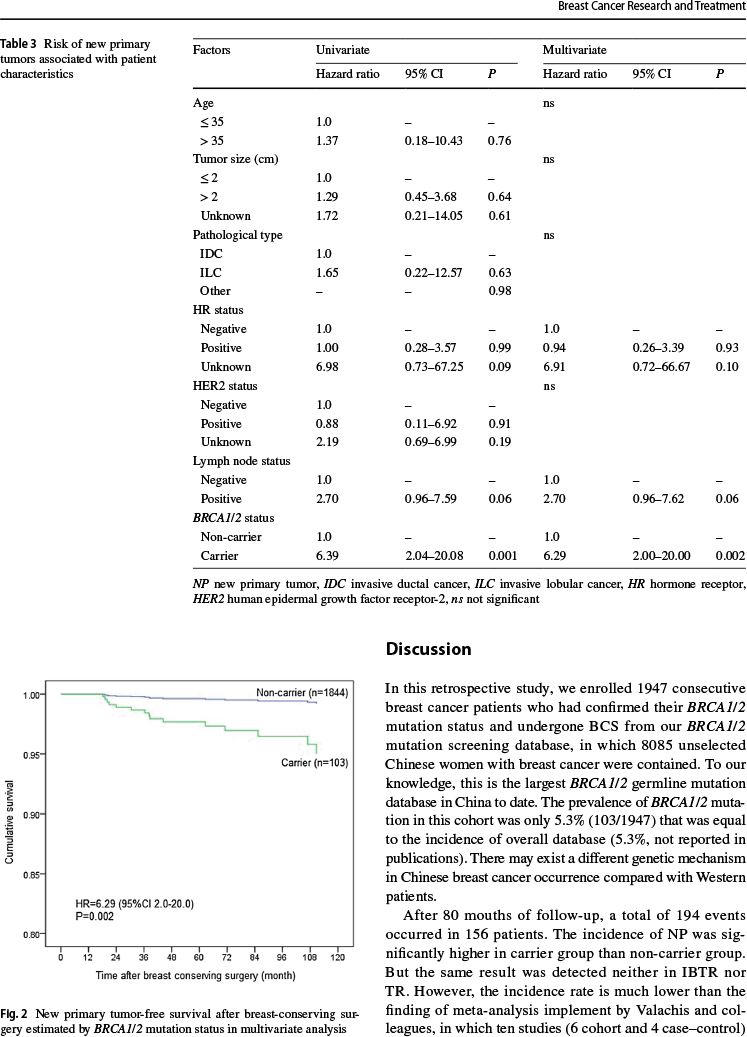
新原发肿瘤的发生率较高:3.9%比0.6%(P<0.01)
对所有临床病理因素进行风险比例分层后,新原发肿瘤的高风险因素包括:
-
突变携带者(风险比:6.29,P=0.002)
-
淋巴结阳性(风险比:2.70,P=0.06)
因此,该研究结果表明,保乳手术可以作为中国BRCA突变携带者的合理选择,将来应该密切关注突变携带者的新原发肿瘤风险。
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Mar 20.
Risk of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence in primary invasive breast cancer following breast-conserving surgery with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation in China.
Wei Cao, Yuntao Xie, Yingjian He, Jinfeng Li, Tianfeng Wang, Zhaoqing Fan, Tie Fan, Tao Ouyang.
Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China.
PURPOSE: BRCA1/2 germline mutations are associated with a high risk of breast cancer, which may preclude mutation carriers from breast-conserving surgery (BCS). This study retrospectively examined whether mutation status influenced the rate of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (IBTR) after BCS in Chinese women.
METHODS: Patients who underwent BCS were enrolled in carriers group and non-carriers group according to their BRCA1/2 mutation status in the study. The correlations were analyzed between IBTR incidence and BRCA1/2 mutation. The IBTR cases were further separated into new primary tumor (NP) and true local recurrences (TR). The risk factors of NP were studied in multivariate analysis.
RESULTS: 1947 consecutive Chinese women with primary invasive breast cancer were selected. 103 patients were identified as BRCA1/2 mutation carriers and 1844 were non-carriers. BRCA1/2 mutation carriers were younger (P<0.001) with more often negative HER-2 expression (P=0.01) and tumor size over 2 cm (P=0.04) than non-carriers. The median follow-up for all patients was 80 months. The rate of IBTR was 3.9% in mutated carriers and 2.0% in non-carriers, respectively (P=0.16). In IBTR cases, NP incidence was 3.9% in carrier group and 0.6% in non-carrier group, respectively (P<0.01). After adjustment of all clinical-pathological factors, BRCA1/2 mutation was the only statistical risk factor of NP incidence (HR=6.29, P=0.002), while positive lymph node was nearly statistically significant (HR=2.70, P=0.06).
CONCLUSIONS: BCS may be a rational option for Chinese BRCA1/2 mutation carriers. High NP incidence in mutation carriers should be paid close attention in the future.
KEYWORDS: Breast cancer Breast-conserving surgery BRCA1/2 mutation Ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence
DOI: 10.1007/s10549-019-05199-8