爱荷华州立大学首次成功报道用CRISPR/Cas9对四倍体柳枝稷进行基因编辑
欢迎点击「植物科学最前沿」↑关注我们!
近日,爱荷华州立大学Dr. Shuizhang Fei团队和Dr. Bing Yang团队在Plant Biotechnology Journal在线发表了题为 “Targeted mutagenesis in tetraploid switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) using CRISPR/Cas9” 的研究论文。该研究通过系统的原生质体和稳定遗传转化实验以及形态学观察分析,首次报道基因编辑工具CRISPR/Cas9系统可以成功对柳枝稷(switchgrass)进行基因组定点编辑。
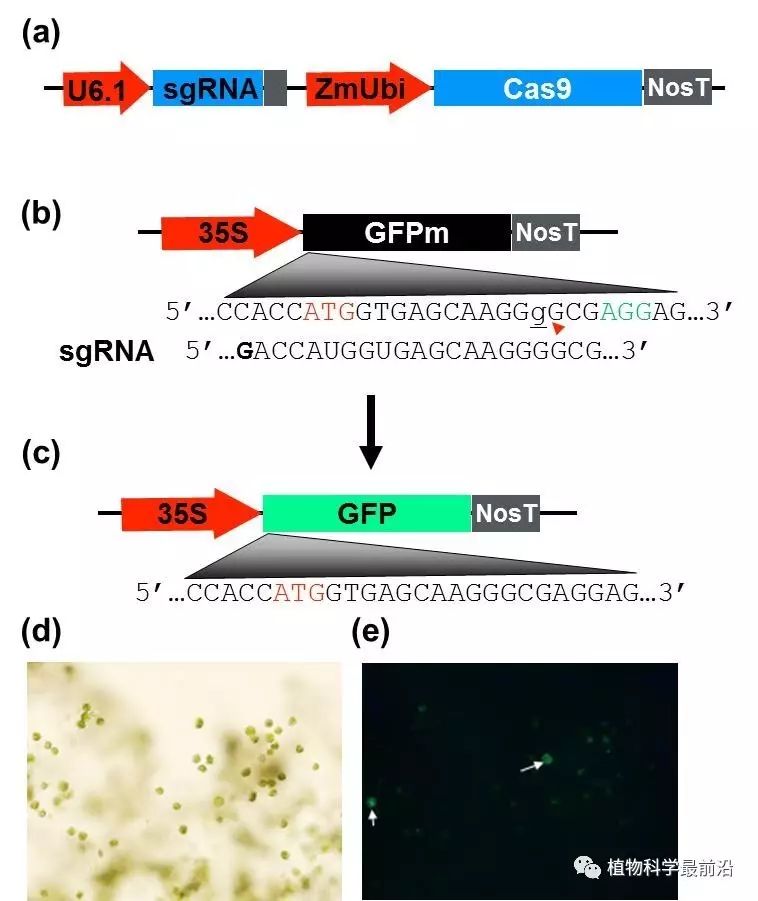
Figure 1. Switchgrass protoplast system for assessing CRISPR/Cas9 activity with the GFP reporter gene.
柳枝稷(Panicum virgatum L.)是重要的生物能源作物,但是由于其复杂的倍性和自交不亲和性,育种和基因功能研究的开展比较困难。因此,开发高效的基因编辑工具对柳枝稷研究具有重大意义。Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)- associated nuclease 9 (CRISPR/Cas9)系统是利用guide RNA引导核酸酶对基因组DNA进行定点编辑,现已广泛用于动植物基因修饰。
Figure 6. Representative plants of wild type (WT) and one mutant line with increased tiller numbers (tb1 #52-1) are shown.
本研究首先利用原生质体证实了可在水稻中有效进行基因编辑的CRISPR/Cas9系统同样可以在柳枝稷中正常工作。随后,作者使用此系统对柳枝稷生长发育相关的基因phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM)和teosinte branched 1(tb1)进行定点编辑,并成功获得了突变体。其中,对PGM基因的编辑效率为13.7%,并在T0代获得了纯合突变体。对tb1a和tb1b基因的编辑效率分别为95.5%和11%,突变体分枝明显增多,对于提高柳枝稷生物产量具有重要意义。
该研究由爱荷华州立大学Dr. Shuizhang Fei 和Dr. Bing Yang团队合作完成,博士研究生刘阳和硕士Paul Merrick为论文共同第一作者。Dr. Shuizhang Fei 和Dr. Bing Yang为论文共同通讯作者。
The CRISPR/Cas9 system has become a powerful tool for targeted mutagenesis. Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) is a high yielding perennial grass species that has been designated as a model biomass crop by the U.S. Department of Energy. The self infertility and high ploidy level make it difficult to study gene function or improve germplasm. To overcome these constraints, we explored the feasibility of using CRISPR/Cas9 for targeted mutagenesis in a tetraploid cultivar ‘Alamo’ switchgrass. We first developed a transient assay by which a non-functional green fluorescent protein gene containing a 1 bp frameshift insertion in its 5’ coding region was successfully mutated by a Cas9/sgRNA complex resulting in its restored function. Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of embryogenic calli derived from mature caryopses averaged a 3.0% transformation efficiency targeting the genes of teosinte branched 1(tb1)a and b and Phosphoglycerate Mutase (PGM). With a single construct containing two sgRNAs targeting different regions of tb1a and tb1b genes, primary transformants (T0) containing CRISPR/Cas9 induced mutations were obtained at frequencies of 95.5% (tb1a) and 11% (tb1b), respectively, with T0 mutants exhibiting increased tiller production. Meanwhile, a mutation frequency of 13.7% was obtained for the PGM gene with a CRISPR/Cas9 construct containing a single sgRNA. Among the PGM T0 mutants, six are heterozygous and one is homozygous for a 1 bp deletion in the target region with no apparent phenotypical alterations. We show that CRISPR/Cas9 system can generate targeted mutagenesis effectively and obtain targeted homozygous mutants in T0 generation in switchgrass, circumventing the need of inbreeding.